TERMINAL BLOCKS
THE BEST INVENTION FOR YOUR CONNECTION: THE TERMINAL BLOCK.

PORTFOLIO EVOLUTION –
PROVEN SERIES STILL AVAILABLE TO ORDER
The following product series will be replaced by a modernized solution as part of our portfolio development. You can find all information on the changeover, availability, successor products, and transition phase here:
LIVE WEBINAR: EFFICIENT CONTROL CABINET PROCESSES WITH SELOS TERMINAL BLOCKS
In this live webinar, you´ll learn how to implement seamless processes with selos terminal blocks from digital planning to finished wiring, including practical optimization approaches for your control cabinet manufacturing.
Available Live Dates
German:
13 April 2026 | 3:00–4:00 PM
29 April 2026 | 10:30–11:30 AM
English:
13 April 2026 | 1:00–2:00 PM
29 April 2026 | 9:00–10:00 AM
All times in CEST
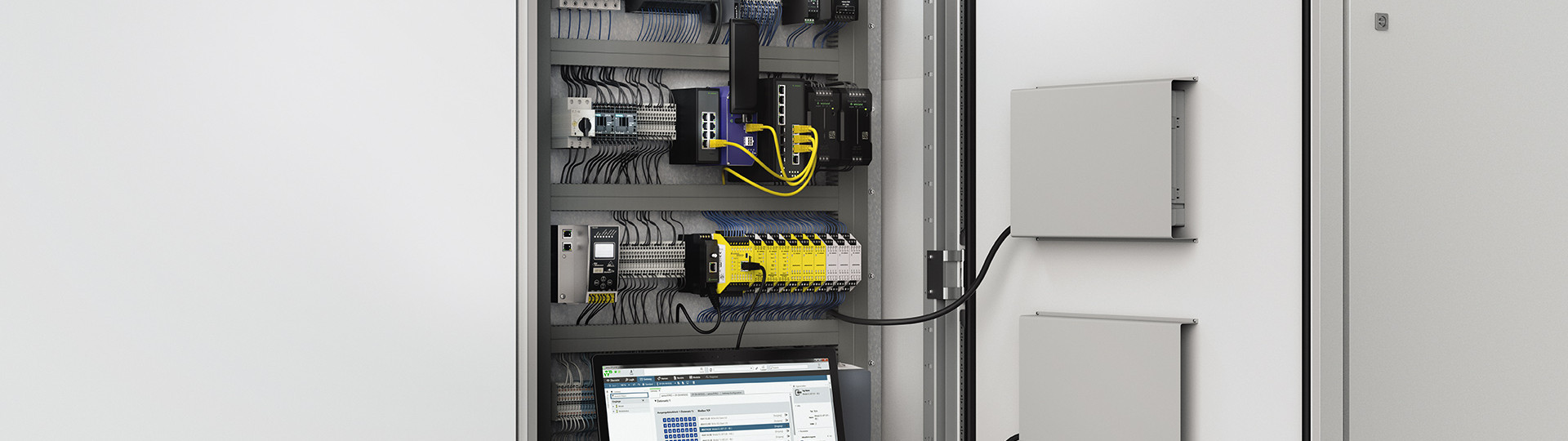
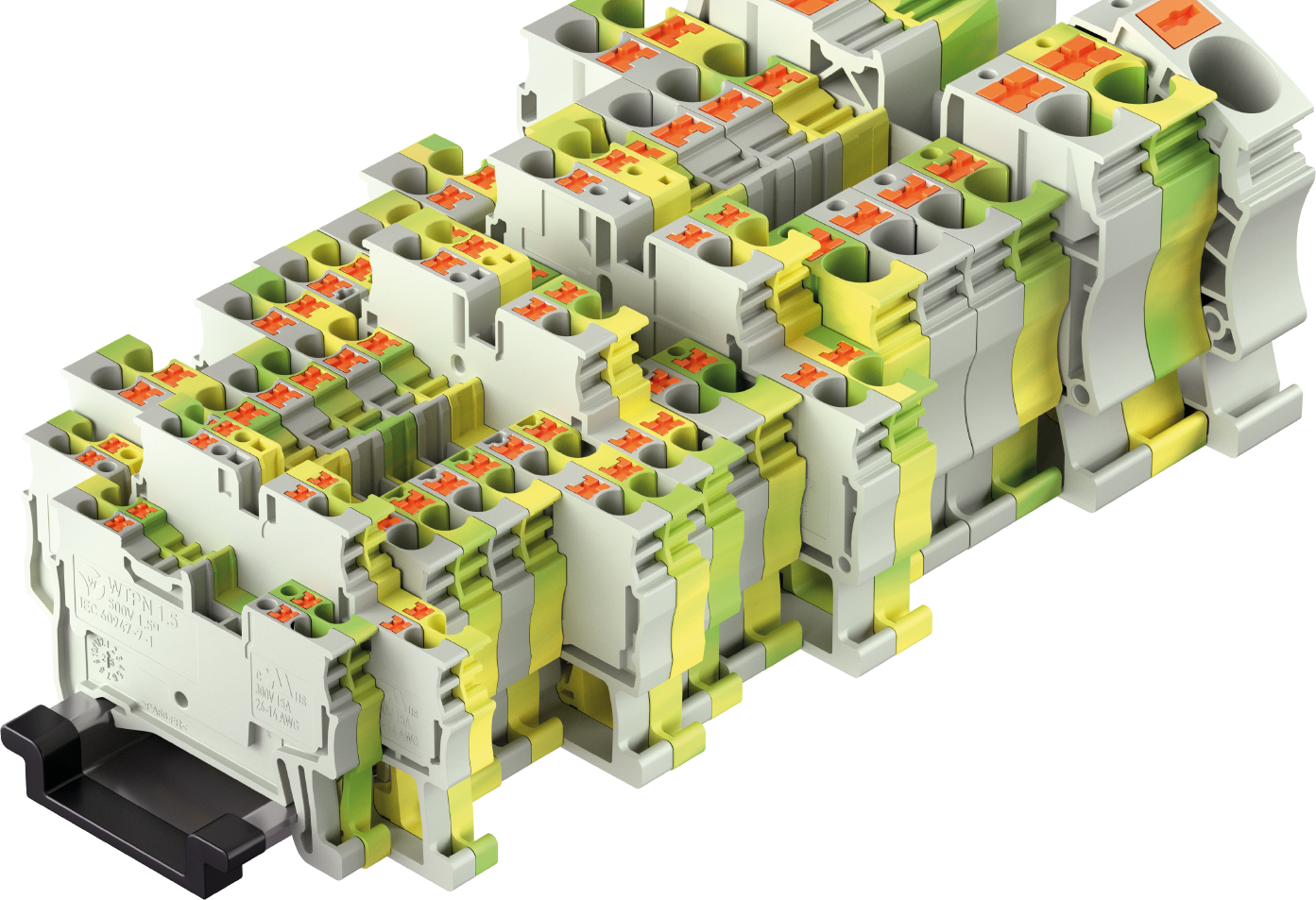
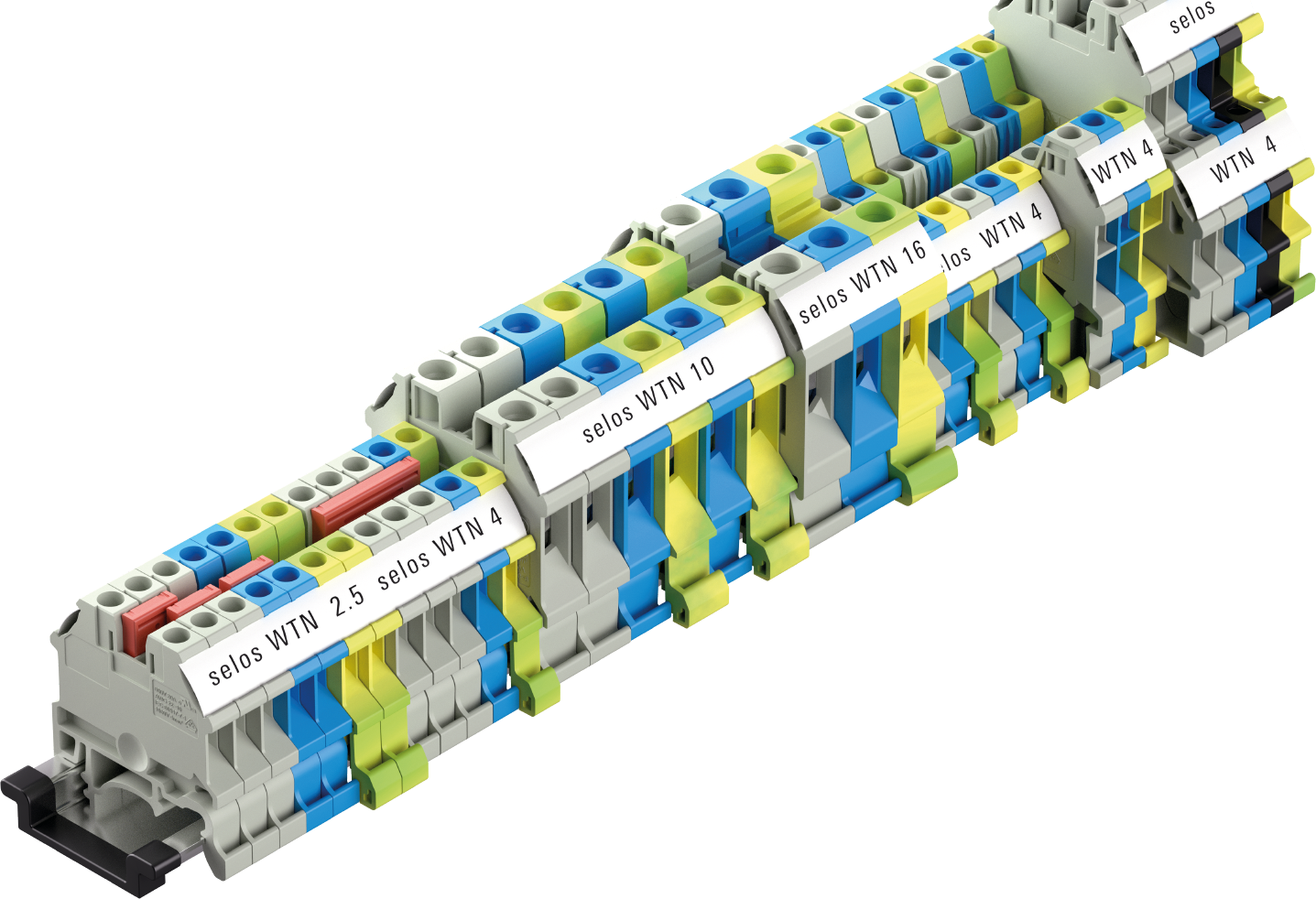
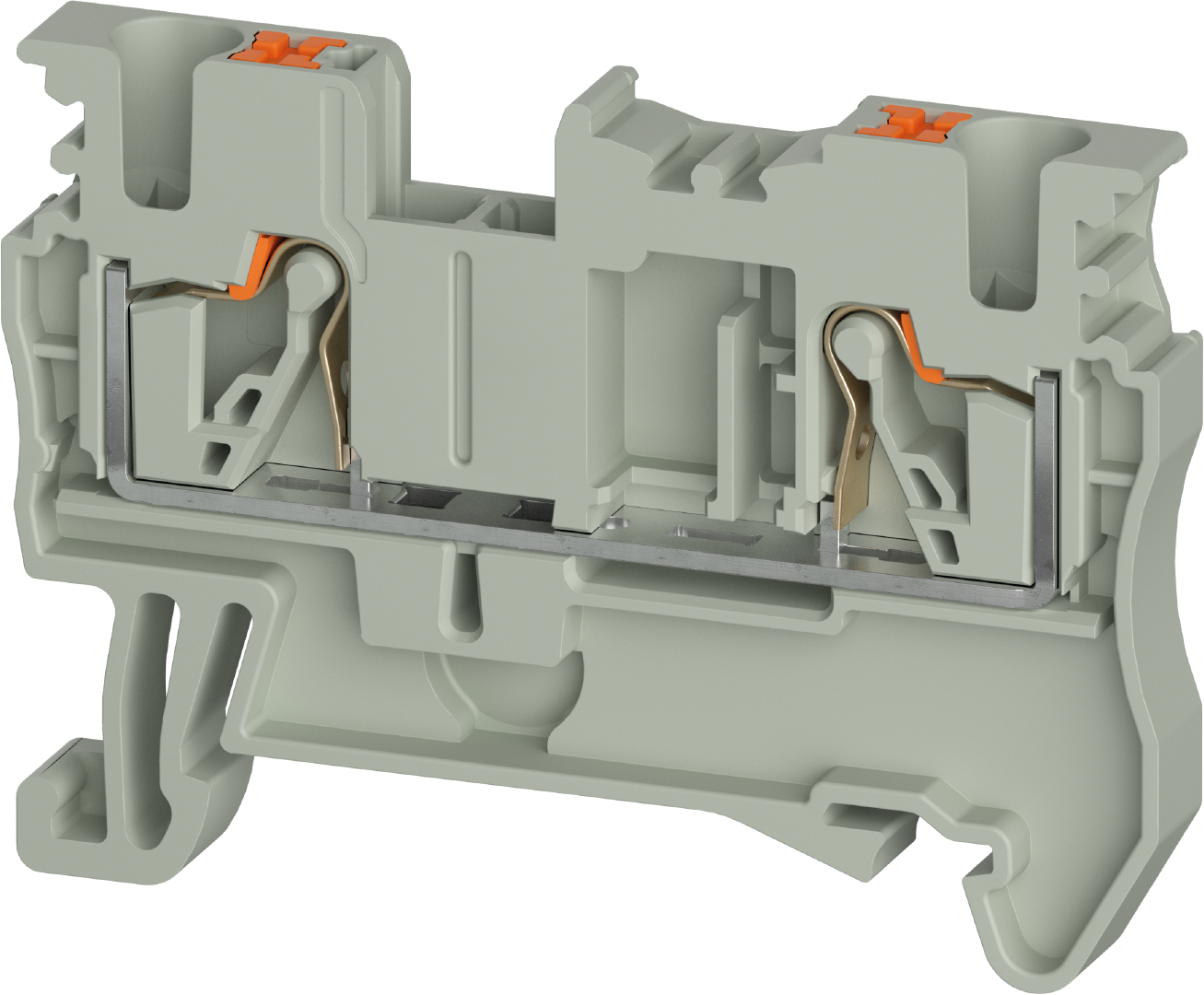
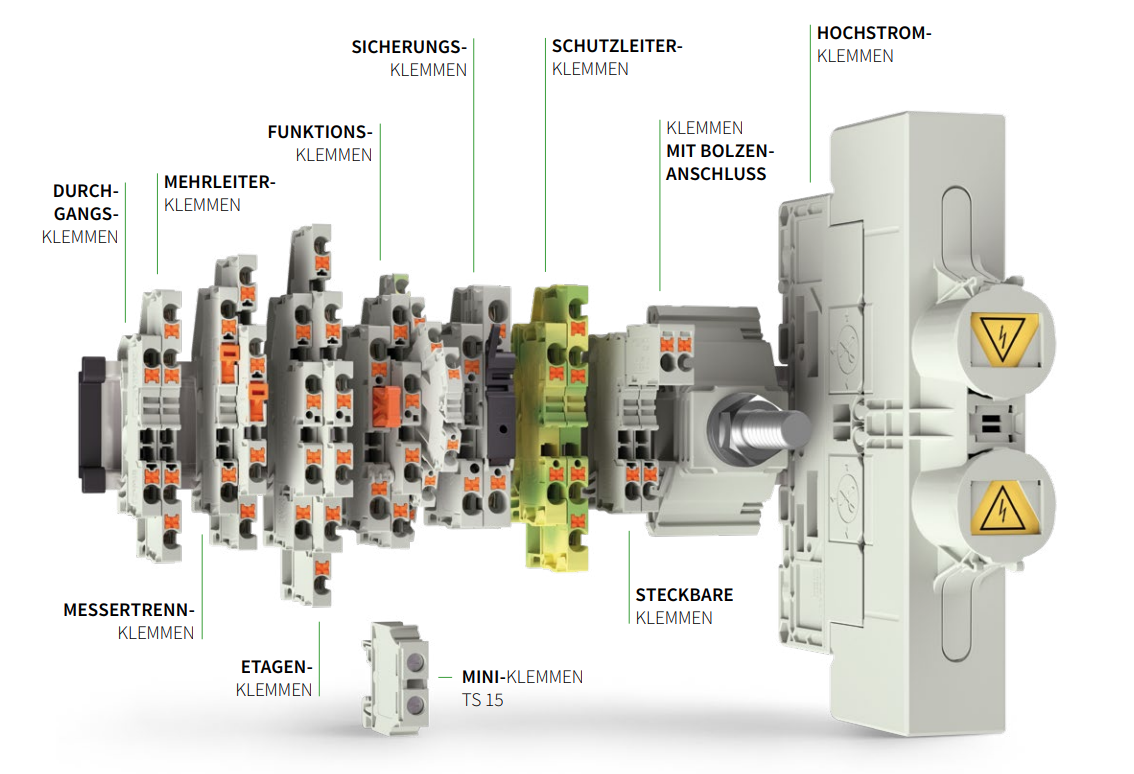
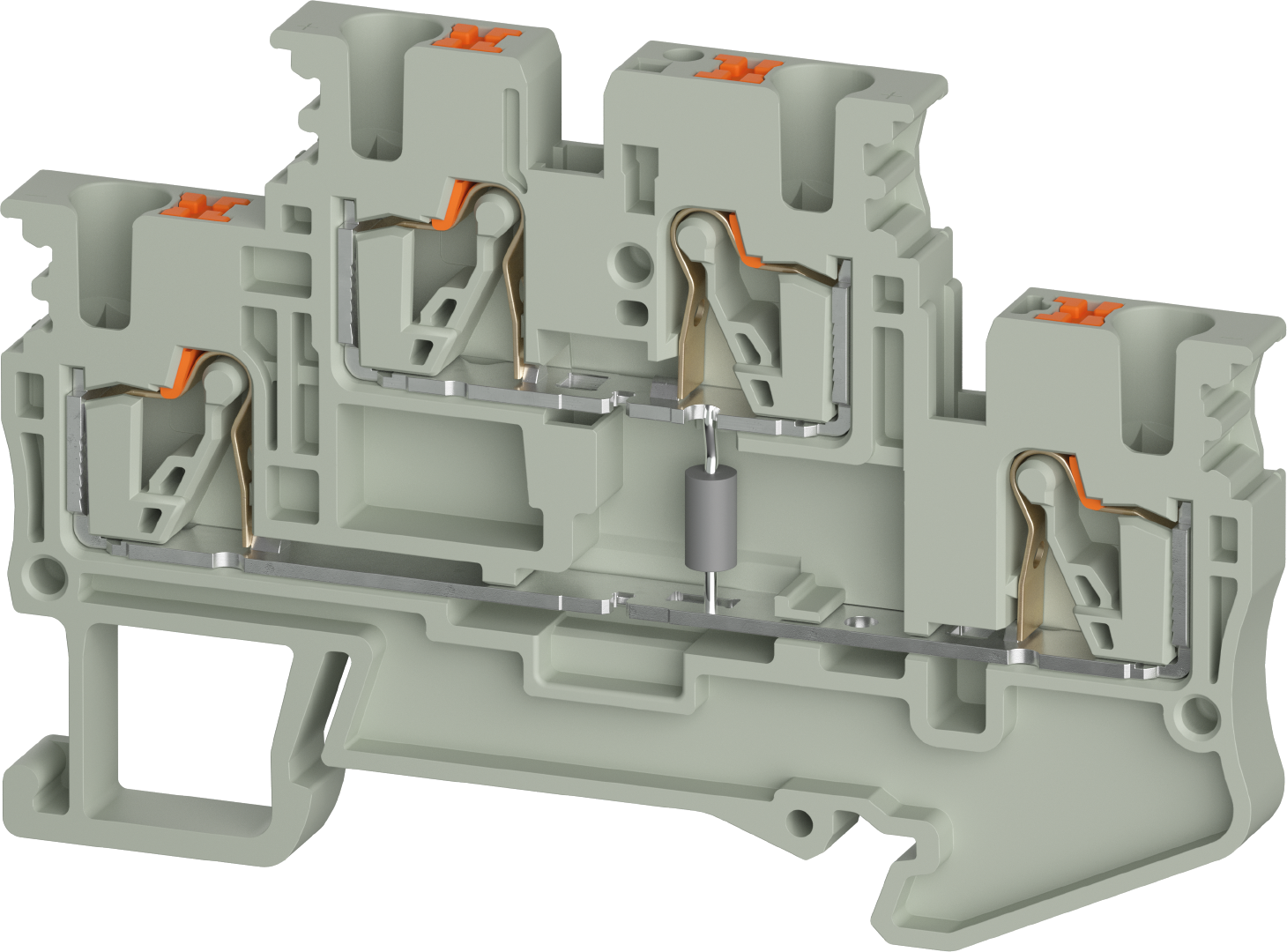
Terminal blocks are electromechanical components used in control cabinets or circuit distribution panels to connect wires, cores, and cables in a detachable and safe manner. When clamped, they distribute power or electrical signals within the control cabinet via a lead.
Terminal blocks are mounted side by side on DIN rails and installed in the control cabinet. Incoming and outgoing conductors from other electrical components or devices are connected to the terminals of the terminal blocks, integrating them into a complex overall system. The essential task of terminal blocks in electrical engineering is to connect electrical conductors and, for example, to control or monitor building installations, power engineering, machines, and systems.
Terminal blocks are used for the connection of conductors at junctions of power and control circuits in power distribution or for the signal distribution of sensors and actuators. The blocks are typically used in control cabinets, where they are mounted on terminal or DIN rails.
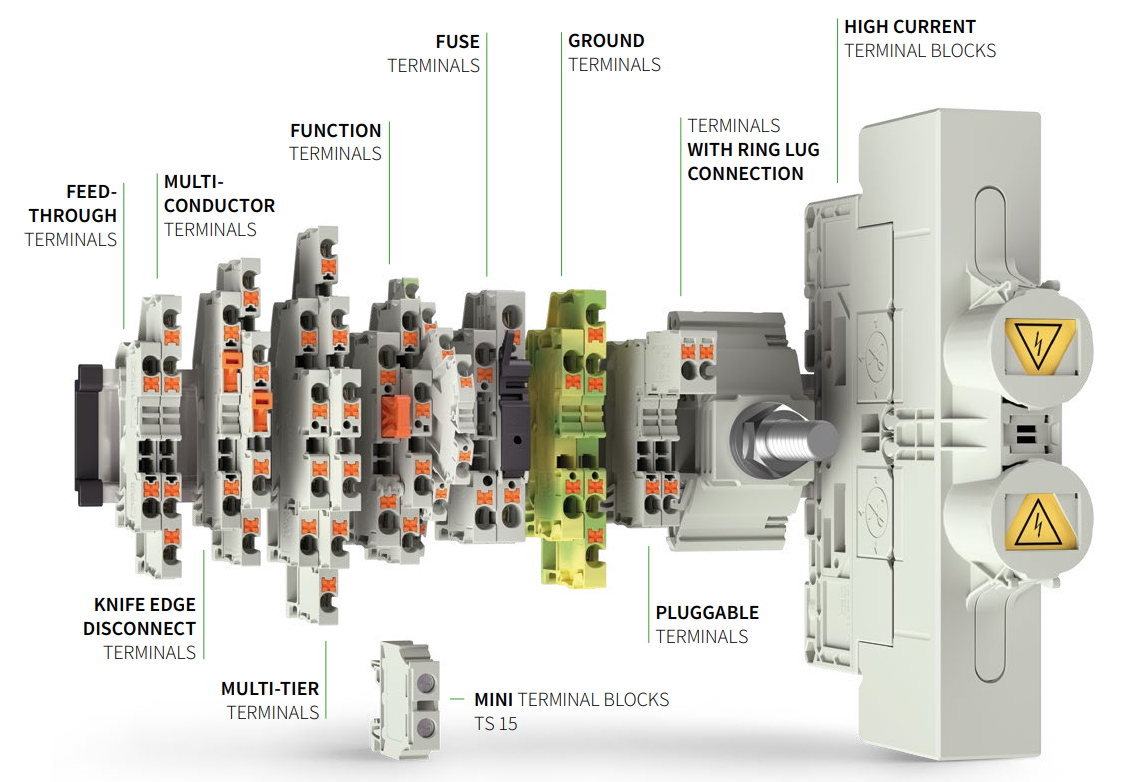
They are differentiated as follows:
- Terminal blocks with small nominal cross section (1.5 mm² and 2.5 mm²), primarily used for sensor signal distribution.
- Terminal blocks with a nominal cross section of 4 mm² or 6 mm²; they are mostly used as terminal blocks for actuators such as pneumatic cylinders, electric motors, and similar.
- Terminal blocks with a nominal cross section of 10 mm² and more are often used for power distribution at higher voltage levels.
In principle, there is no universally applicable legal obligation in Germany to use terminal blocks. However, there are exceptions for special applications—such as the construction of electrical installations in fire-hazardous workplaces. According to DIN VDE 0105-100/A1, electrical installations must be repeatedly tested. An essential test aspect is the so-called insulation measurement, e.g., between neutral conductor and yellow/green conductor. For this measurement, it is necessary to disconnect the neutral conductor of each circuit. Therefore, DIN VDE 0100-718 and VdS 2033 require the use of N-disconnect terminal blocks in public facilities, commercial or industrial workplaces, and fire-hazardous workplaces.
How many terminal blocks you can place at most on a DIN rail (top hat rail) depends on terminal type, connection technology, and conductor cross-section. In practice, it is often neither sensible nor necessary to push the theoretically possible maximum number of terminal blocks on a terminal strip to the limit. A structured layout with sufficient clearances is better. This makes assembly and modification, maintenance, and inspection easiest, and keeps things clear in the control cabinet.